- Installing GitLab Runner
Sep 16, 2020 Make sure you have installed the NVIDIA driver and Docker engine for your Linux distribution Note that you do not need to install the CUDA Toolkit on the host system, but the NVIDIA driver needs to be installed. For instructions on getting started with the NVIDIA Container Toolkit, refer to the installation guide.
We provide packages for the currently supported versions of Debian, Ubuntu, Mint, RHEL, Fedora, and CentOS. You may be able to install GitLab Runner as a binary on other Linux distributions.| Distribution | Version | End of Life date |
|---|---|---|
| Debian | stretch | June 2022 |
| Debian | buster | June 2024 |
| Ubuntu | xenial | April 2021 |
| Ubuntu | bionic | April 2023 |
| Ubuntu | focal | April 2025 |
| Mint | sarah, serena, sonya, sylvia | April 2021 |
| Mint | tara, tessa, tina, tricia | April 2023 |
| Mint | ulyana, ulyssa | April 2025 |
| RHEL/CentOS | 7 | June 2024 |
| CentOS | 8 | December 2021 |
| RHEL | 8 | May 2029 |
| Fedora | 32 | approx. May 2021 |
| Fedora | 33 | approx. Nov 2021 |
Prerequisites
If you want to use the Docker executor, make sure to install Docker beforeusing GitLab Runner. Read how to install Docker for your distribution.
Installing GitLab Runner
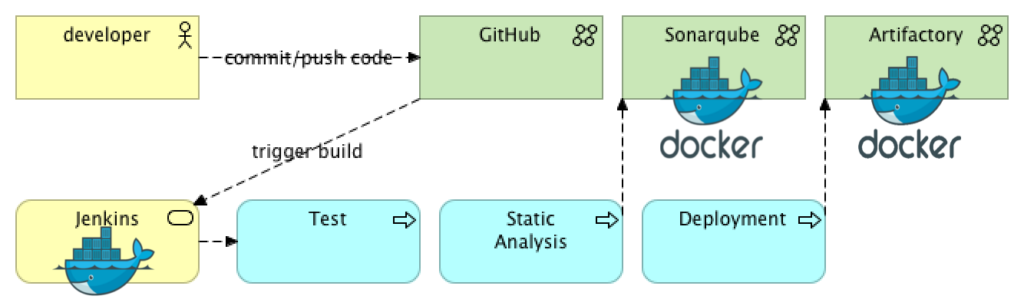
- Install and register GitLab Runner for autoscaling with Docker Machine The auto scale feature was introduced in GitLab Runner 1.1.0. For an overview of the autoscale architecture, take a look at the comprehensive documentation on autoscaling.
- To install Docker on Kali you need to remember that there is already a package named “docker”, therefore Docker has to be installed under a different name. If you install docker you will not end up with the container version. The version we will be installing is named docker.io. All commands are the same however, so running docker on the command line will be the appropriate command.
- Aug 13, 2018 First of all, lets install gitlab-runner via bre w and then we must register gitlab-runner by url and token that is in Setup a specific Runner manually section in Project Settings CI / CD tab.
- If you want to use the Docker executor, make sure to install Docker before using GitLab Runner. Read how to install Docker for your distribution. Installing GitLab Runner.
Gitlab Docker How To
To install GitLab Runner:
Add the official GitLab repository:
Install the latest version of GitLab Runner, or skip to the next step toinstall a specific version:
Debian buster users should disable skel to preventNo such file or directory JobfailuresTo install a specific version of GitLab Runner:
After completing the step above, a runner should be started and beready to be used by your projects!
Make sure that you read the FAQ section which describessome of the most common problems with GitLab Runner.
APT pinning
A native package called gitlab-ci-multi-runner is available inDebian Stretch. By default, when installing gitlab-runner, that packagefrom the official repositories will have a higher priority.
If you want to use our package, you should manually set the source ofthe package. The best way is to add the pinning configuration file.
If you do this, the next update of the GitLab Runner package - whether it willbe done manually or automatically - will be done using the same source:
Updating GitLab Runner
Simply execute to install latest version:
Manually download packages
You can manually download and install thepackages if necessary.
Disable skel
Introduced in GitLab 12.10.
Sometimes the default skeleton (skel) directorycauses issues for GitLab Runner,and it fails to run a job. When installing GitLab Runner, set the environment variableGITLAB_RUNNER_DISABLE_SKEL to true before you install the package. This will createthe $HOME directory without the files inside of skel:
For example:
Upgrading to GitLab Runner 10
To upgrade GitLab Runner from a version prior to 10.0:
Remove the old repository:
Follow the same steps when installing GitLab Runner,without registering it and using the new repository.
For RHEL/CentOS/Fedora, run:
If you don’t run the above command, you will be leftwith no service file. Follow issue #2786for more information.
Help & feedback
Docs
Edit this pageto fix an error or add an improvement in a merge request.Create an issueto suggest an improvement to this page.
Show and post commentsto review and give feedback about this page.
Product
Create an issueif there's something you don't like about this feature.Propose functionalityby submitting a feature request.
Join First Lookto help shape new features.
Feature availability and product trials
View pricingto see all GitLab tiers and features, or to upgrade.Try GitLab for freewith access to all features for 30 days.
Get Help
If you didn't find what you were looking for,search the docs.
If you want help with something specific and could use community support,post on the GitLab forum.
For problems setting up or using this feature (depending on your GitLabsubscription).
- Using the forked version of Docker Machine
- Using GPUs on Google Compute Engine
The auto scale feature was introduced in GitLab Runner 1.1.0.
For an overview of the autoscale architecture, take a look at thecomprehensive documentation on autoscaling.
Forked version of Docker machine
Because docker-machine is in maintenancemode, GitLab isproviding it’s own fork ofdocker-machine,which is based on the latest master branch of docker-machine withsome additional patches for the following bugs:
The intent of this fork is to fix critical and bugs affecting runningcosts only. No new features will be added.
Preparing the environment
To use the autoscale feature, Docker and GitLab Runner must beinstalled in the same machine:
- Log in to a new Linux-based machine that will serve as a bastion serverwhere Docker will spawn new machines from
- Optionally but recommended, prepare aproxy container registry and a cache serverto be used with the autoscaled runners
If you need to use any virtualization/cloud providers that aren’t handled byDocker Machine’s internal drivers, the appropriate driver plugin must beinstalled. The Docker Machine driver plugin installation and configuration isout of the scope of this documentation. For more details please read theDocker Machine documentation
Configuring GitLab Runner
- Register a runner and select the
docker+machineexecutor when asked. - Edit
config.tomland configurethe runner to use Docker machine. Visit the dedicated page covering detailedinformation about GitLab Runner Autoscaling. The first time you’re using Docker Machine, it’s best to execute manually
docker-machine create ...with your chosen driver and all options from theMachineOptionssection. This will set up the Docker Machine environmentproperly and will also be a good validation of the specified options.After this, you can destroy the machine withdocker-machine rm [machine_name]and start the runner.Multiple concurrent requests todocker-machine createthat are doneat first usage are not good. When thedocker+machineexecutor is used,the runner may spin up few concurrentdocker-machine createcommands. IfDocker Machine was not used before in this environment, each started processtries to prepare SSH keys and SSL certificates (for Docker API authenticationbetween GitLab Runner and Docker Engine on the autoscaled spawned machine), and theseconcurrent processes are disturbing each other. This can end with a non-workingenvironment. That’s why it’s important to create a test machine manually thevery first time you set up GitLab Runner with Docker Machine.- Now, you can try and start a new pipeline in your project. In a few seconds,if you run
docker-machine lsyou should see a new machine being created.
Upgrading GitLab Runner
- Check if your operating system is configured to automatically restart GitLabRunner (for example, by checking its service file):
if yes, ensure that service manager is configured to use
SIGQUITand use the service’s tools to stop the process:if no, you may stop the process manually:
Sending theSIGQUITsignal will make theprocess stop gracefully. The process will stop accepting new jobs, and will exitas soon as the current jobs are finished. Wait until GitLab Runner exits. You can check its status with
gitlab-runner statusor await a graceful shutdown for up to 30 minutes with:- You can now safely install the new version of GitLab Runner without interrupting any jobs.
Using the forked version of Docker Machine
Install
Download the appropriate
docker-machinebinary.Copy the binary to a location accessible toPATHand make itexecutable. For example, to download and installv0.16.2-gitlab.11:
Using GPUs on Google Compute Engine
Introduced in GitLab Docker Machine 0.16.2-gitlab.10 and GitLab Runner 13.9.
You can use the Docker Machine fork to create Google Compute Engine instanceswith graphics processing units (GPUs).GitLab Runner 13.9 is required for GPUs to work in a Docker executor.
Docker Machine GPU options
To create an instance with GPUs, use these Docker Machine options:| Option | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
--google-accelerator | type=nvidia-tesla-p4,count=1 | Specifies the type and number of GPU accelerators to attach to the instance (type=TYPE,count=N format) |
--google-maintenance-policy | TERMINATE | Always use TERMINATE because Google Cloud does not allow GPU instances to be live migrated. |
--google-machine-image | https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/deeplearning-platform-release/global/images/family/tf2-ent-2-3-cu110 | The URL of a GPU-enabled operating system. See the list of available images. |
--google-metadata | install-nvidia-driver=True | This flag tells the image to install the NVIDIA GPU driver. |
These arguments map to command-line arguments for gcloud compute.See the Google documentation on creating VMs with attached GPUsfor more details.
Verifying Docker Machine options
To prepare your system and test that GPUs can be created with Google Compute Engine:
Set up the Google Compute Engine driver credentialsfor Docker Machine. You may need to export environment variables to therunner if your VM does not have a default service account. Howthis is done depends on how the runner is launched. For example:
- Via
systemdorupstart: See the documentation on setting custom environment variables. - Via Kubernetes with the Helm Chart: Update the
values.yamlentry. - Via Docker: Use the
-eoption (for example,docker run -e GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS=/path/to/credentials.json gitlab/gitlab-runner).
- Via
Verify that
docker-machinecan create a virtual machine with yourdesired options. For example, to create ann1-standard-1machinewith a single NVIDIA Telsa P4 accelerator, substitutetest-gpuwith a name and run:To verify the GPU is active, SSH into the machine and run
nvidia-smi:Remove this test instance to save money:
Configuring GitLab Runner
Once you have verified these options, configure the Docker executorto use all available GPUs in the
runners.dockerconfiguration.Then add the Docker Machine options to yourMachineOptionssettings in the GitLab Runnerrunners.machineconfiguration. For example:
Help & feedback
Docs
Edit this pageto fix an error or add an improvement in a merge request.Create an issueto suggest an improvement to this page.
Show and post commentsto review and give feedback about this page.
Product
Create an issueif there's something you don't like about this feature.Propose functionalityby submitting a feature request.
Join First Lookto help shape new features.
Feature availability and product trials
View pricingto see all GitLab tiers and features, or to upgrade.Try GitLab for freewith access to all features for 30 days.
Get Help
Docker Install Gitlab Failed
If you didn't find what you were looking for,search the docs.
If you want help with something specific and could use community support,post on the GitLab forum.
For problems setting up or using this feature (depending on your GitLabsubscription).
Docker Install Gitlab Ubuntu
 Please enable JavaScript to view thecomments powered by Disqus.
Please enable JavaScript to view thecomments powered by Disqus.